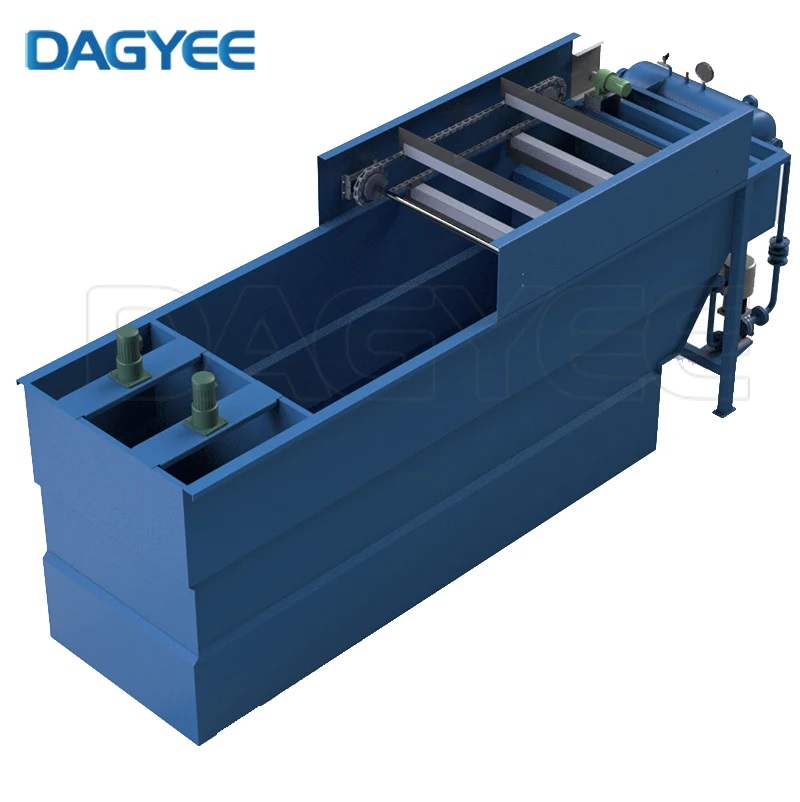


Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) units play a pivotal role in modern wastewater treatment processes. These units are designed to remove suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants from wastewater by injecting air into the water under pressure. Once the pressure is released, tiny air bubbles interact with the suspended particles, causing them to float to the surface where they can be easily skimmed off. This process results in the production of clarified water which is then directed to the bottom of the flotation chamber and collected at an effluent control weir. By efficiently separating impurities, DAF units enhance the quality of treated water and ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
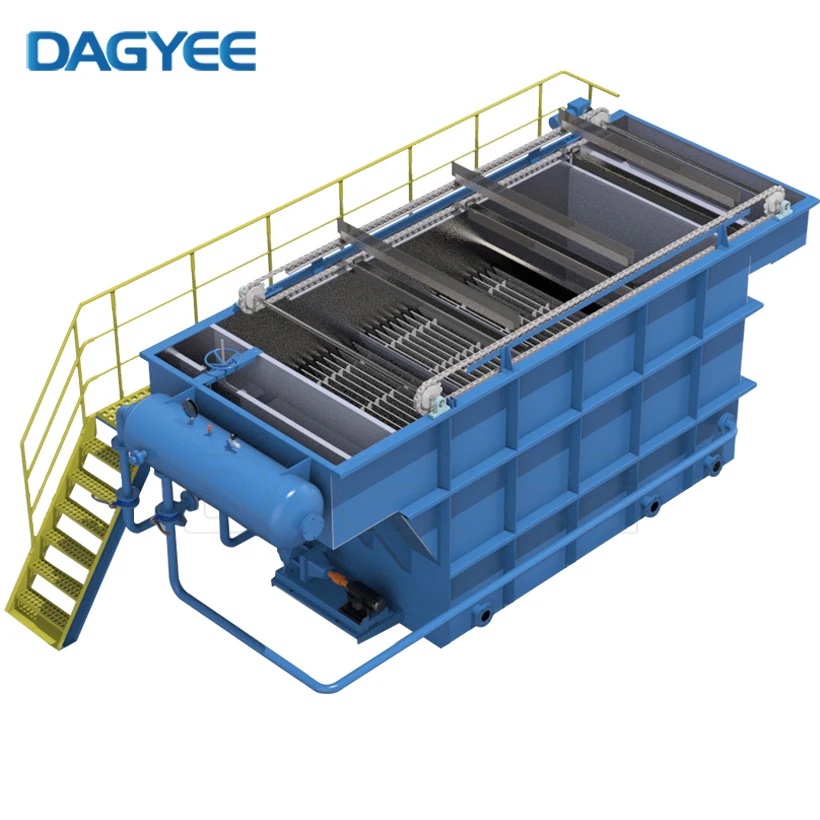

1. Presaturation
The initial step involves saturating the wastewater with air under pressure. In a pressure vessel, air is dissolved in the water at pressures ranging from 3 to 6 atmospheres, which results in a high concentration of dissolved air.
2. Release of Pressure and Formation of Bubbles
Once the pressurized air-saturated water is released into the flotation tank, the pressure drop causes the air to precipitate as fine bubbles. These micro-bubbles (typically 30-50 micrometers in diameter) adhere to the suspended particles in the water.
3. Flotation
As the bubbles rise, they carry the attached particles to the surface of the flotation tank. This creates a floating layer of sludge on the surface, which can then be mechanically skimmed off.
4. Sedimentation
The clarified water, now largely free of suspended solids, is discharged from the bottom of the flotation tank, often going on to further treatment or being discharged as final effluent.
Dissolved air flotation technical sheet
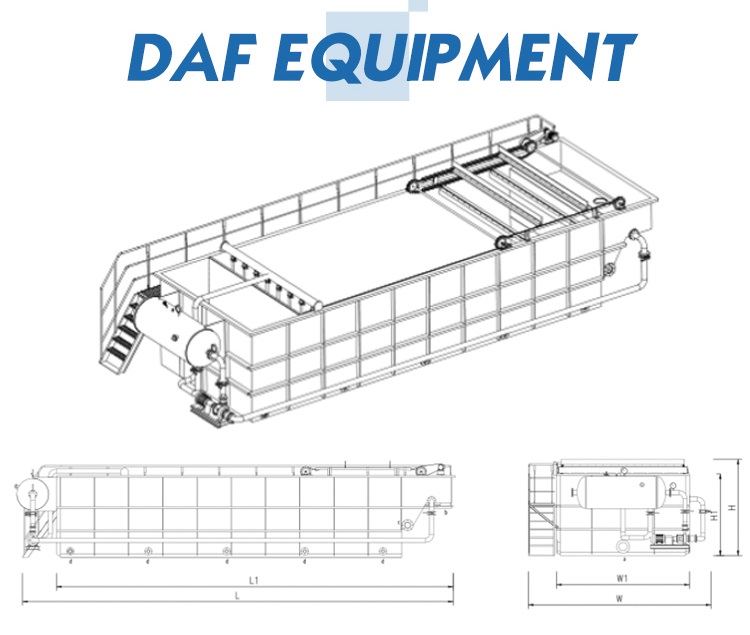
| DAF Model | Qm3/h | Piping Connections | Physical Dimensions(m) | Weight (Kg) | Operating Weight (Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAF-003 | 3 |
Inlet: DN50 Outlet: DN50 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 3.7/2.8 W/W1: 2.4/1.16 H/H1: 2.2/1.7 |
1500 | 5000 |
| DAF-005 | 5 |
Inlet: DN80 Outlet: DN80 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN80 |
L/L1: 4/3 W/W1: 2.4/1.16 H/H1: 2.2/1.7 |
1600 | 7000 |
| DAF-010 | 10 |
Inlet: DN100 Outlet: DN100 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 4.65/3.8 W/W1: 2.7/1.36 H/H1: 2.4/1.9 |
2000 | 12000 |
| DAF-015 | 15 |
Inlet: DN125 Outlet: DN100 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 5.6/4.5 W/W1: 2.9/1.66 H/H1: 2.5/2 |
2200 | 18000 |
| DAF-020 | 20 |
Inlet: DN150 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 5.9/4.8 W/W1: 3.2/1.96 H/H1: 2.5/2 |
3000 | 22000 |
| DAF-030 | 30 |
Inlet: DN150 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 6.8/5.5 W/W1: 3.2/2.16 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
3800 | 32000 |
| DAF-040 | 40 |
Inlet: DN200 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 8/6.7 W/W1: 3.6/2.6 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
5000 | 45000 |
| DAF-050 | 50 |
Inlet: DN200 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 8.4/7 W/W1: 3.6/2.6 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
5500 | 55000 |
| DAF-060 | 60 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN200 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 9.9/8.4 W/W1: 3.8/2.8 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
6000 | 66000 |
| DAF-070 | 70 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN200 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 10.4/9 W/W1: 3.8/2.8 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
6500 | 75000 |
| DAF-080 | 80 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 10.8/9.4 W/W1: 4/3 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
7500 | 100000 |
| DAF-100 | 100 |
Inlet: DN300 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 12.1/10.6 W/W1: 4.2/3.2 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
9000 | 110000 |
| DAF-120 | 120 |
Inlet: DN300 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 12.5/11.4 W/W1: 4.4/3.4 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
10000 | 130000 |
Dissolved air flotation process flow


High Efficiency in Solid Removals: DAF can remove over 90% of suspended solids and fats, oils, and greases (FOG), making it highly effective for industrial applications.
Compact Design: The overall size of DAF units is relatively smaller compared to sedimentation tanks, allowing them to fit into facilities where space is a premium.
Versatile Application: DAF systems can treat various types of wastewater across different industries, including food and beverage, oil and gas, and pulp and paper.
Short Hydraulic Retention Time: The process is relatively fast, offering significant reductions in processing time compared to sedimentation methods.
Ease of Operation and Delimitation of Sludges: The floating sludge is easier to collect and process for further treatment or disposal.

The continuous evolution of DAF technology is driven by the need for greater efficiency and sustainability.
Energy Efficiency: Advances focus on reducing energy consumption through improved aeration systems and optimized flotation models. The development of ultra-fine bubble generators enables more efficient bubble-particle aggregation.
Chemical Dosing Optimization: Use of coagulant and flocculant aids in improving the agglomeration of particles prior to flotation, enhancing the removal efficiency and reducing chemical usage.
Automation and Control Systems: Modern DAF units often incorporate sophisticated control systems for optimizing operation, facilitating real-time monitoring and adjustment of process parameters to ensure optimal performance.
Dissolved air flotation application
DAF systems find applicability across multiple industrial sectors, addressing specific water treatment needs.
1. Municipal Wastewater Treatment
In municipal settings, DAF systems are utilized for primary treatment to remove floatable solids. They play a key role in reducing BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) and TSS (Total Suspended Solids) concentrations, ensuring the water meets regulatory discharge standards.
2. Industrial Water Treatment
Various industries employ DAF technology to manage their wastewater:
Food and Beverage Industry: Efficiently removes FOG and other organic solids from food processing wastewater, thereby protecting subsequent treatment processes.
Pulp and Paper Industry: Essential in reducing chemical oxygen demand (COD), DAF units help remove cellulose fibers and other suspended materials from wastewater streams.
Oil and Gas Industry: DAF is crucial for separating hydrocarbons from produced water, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and facilitating safer disposal or reuse.
3. Pretreatment for Membrane Filtration
DAF systems are often used as a pretreatment step before membrane filtration. By significantly reducing suspended solids, DAF improves membrane lifespan and performance in processes like ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis.

Contact Us for a Consultation

Name: Ashely Li
Mobile:+8613961861780
Tel:+8613961861780
Whatsapp:8613961861780
Email:info@dagyee.com
Add:Room 302, Building 11-4, Hongyi Road, Xinan Town, Xinwu District, jiangsu Province, China