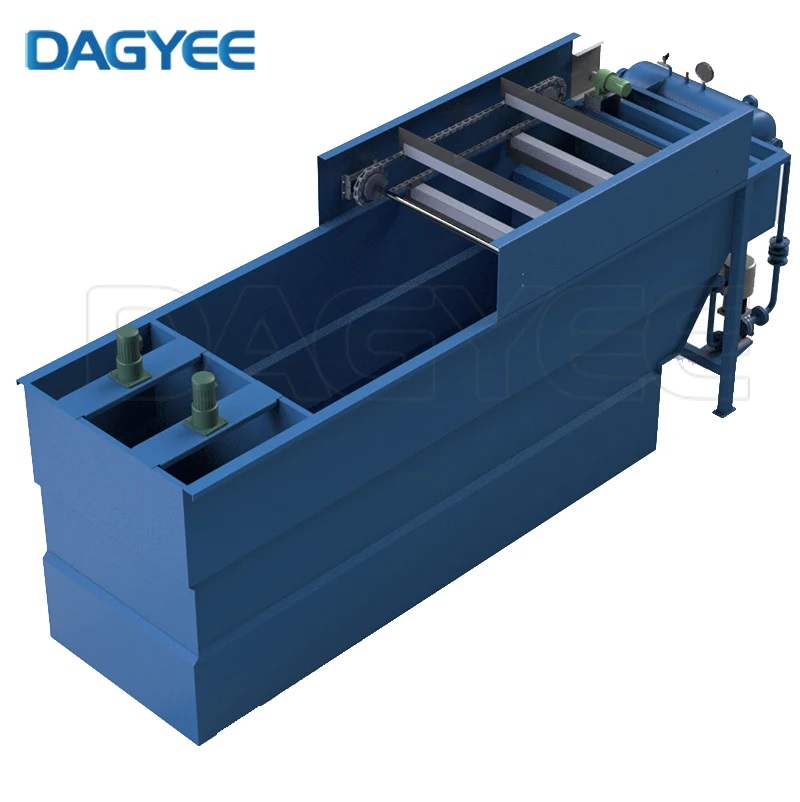


Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) units play a pivotal role in modern wastewater treatment processes. These units are designed to remove suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants from wastewater by injecting air into the water under pressure. Once the pressure is released, tiny air bubbles interact with the suspended particles, causing them to float to the surface where they can be easily skimmed off. This process results in the production of clarified water which is then directed to the bottom of the flotation chamber and collected at an effluent control weir. By efficiently separating impurities, DAF units enhance the quality of treated water and ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
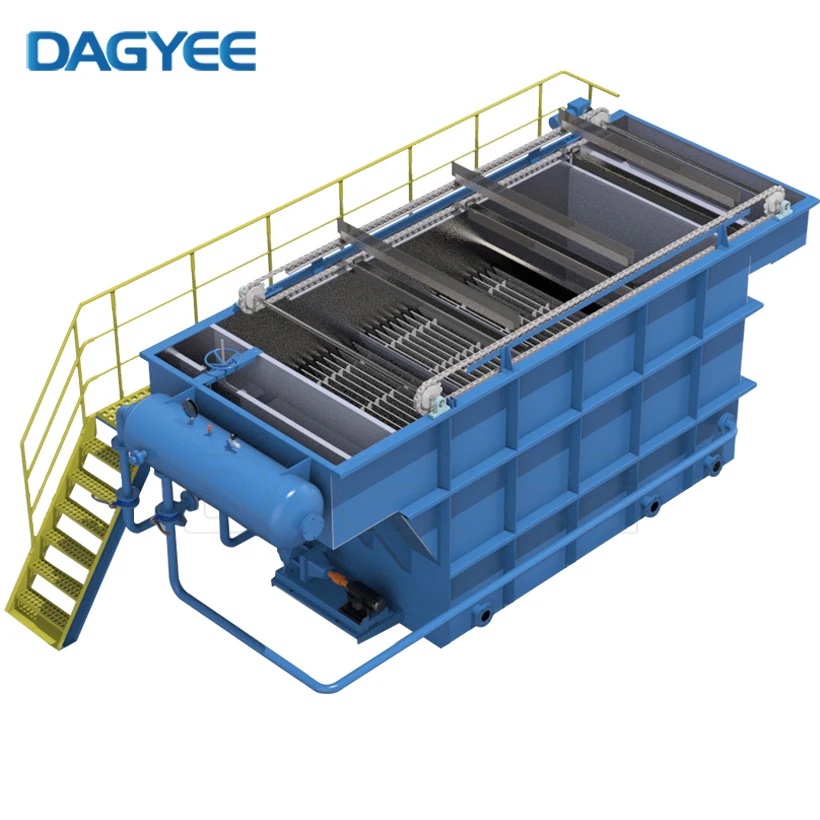

Dissolved Air Flotation is a fairly simple technology using pressurised air to remove small solids, oils, and greases from wastewater. The physical process happens as follows:
Pressurised air is mixed with pressurised water. Due to the higher pressure, more air is able to dissolve into the water. Pumps with a high energy output are able to achieve complete air saturation of the water.
The pressure control valve causes the high pressure to drop to low. The resulting drop in pressure means that the water is now suddenly over-saturated (supersaturated) with air.
The excess air molecules start to cluster together at existing nucleation sites such as small particles or longer-chain molecules, or surface-active molecule. Since the water is supersaturated instantaneously, the clusters of air molecules stay small, forming very small bubbles.
Buoyancy now causes the bubbles to rise, taking the contaminants with them. Generally, the surface tension of the water keeps particles incased in bubbles once they reach the top of the tank, causing a foam to form which can be easily removed.
Dissolved air flotation technical sheet
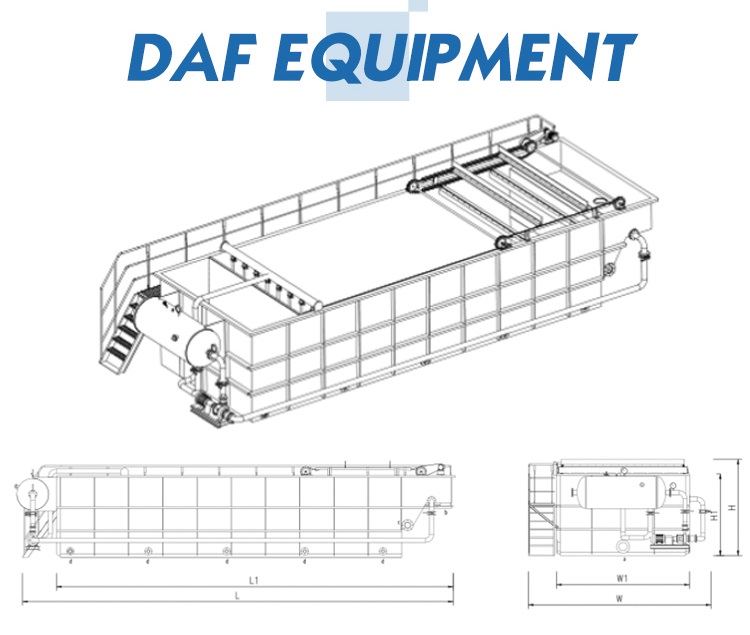
| DAF Model | Qm3/h | Piping Connections | Physical Dimensions(m) | Weight (Kg) | Operating Weight (Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAF-003 | 3 |
Inlet: DN50 Outlet: DN50 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 3.7/2.8 W/W1: 2.4/1.16 H/H1: 2.2/1.7 |
1500 | 5000 |
| DAF-005 | 5 |
Inlet: DN80 Outlet: DN80 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN80 |
L/L1: 4/3 W/W1: 2.4/1.16 H/H1: 2.2/1.7 |
1600 | 7000 |
| DAF-010 | 10 |
Inlet: DN100 Outlet: DN100 Sludge: DN100 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 4.65/3.8 W/W1: 2.7/1.36 H/H1: 2.4/1.9 |
2000 | 12000 |
| DAF-015 | 15 |
Inlet: DN125 Outlet: DN100 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 5.6/4.5 W/W1: 2.9/1.66 H/H1: 2.5/2 |
2200 | 18000 |
| DAF-020 | 20 |
Inlet: DN150 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 5.9/4.8 W/W1: 3.2/1.96 H/H1: 2.5/2 |
3000 | 22000 |
| DAF-030 | 30 |
Inlet: DN150 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 6.8/5.5 W/W1: 3.2/2.16 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
3800 | 32000 |
| DAF-040 | 40 |
Inlet: DN200 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 8/6.7 W/W1: 3.6/2.6 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
5000 | 45000 |
| DAF-050 | 50 |
Inlet: DN200 Outlet: DN150 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 8.4/7 W/W1: 3.6/2.6 H/H1: 2.7/2.2 |
5500 | 55000 |
| DAF-060 | 60 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN200 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 9.9/8.4 W/W1: 3.8/2.8 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
6000 | 66000 |
| DAF-070 | 70 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN200 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 10.4/9 W/W1: 3.8/2.8 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
6500 | 75000 |
| DAF-080 | 80 |
Inlet: DN250 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 10.8/9.4 W/W1: 4/3 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
7500 | 100000 |
| DAF-100 | 100 |
Inlet: DN300 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 12.1/10.6 W/W1: 4.2/3.2 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
9000 | 110000 |
| DAF-120 | 120 |
Inlet: DN300 Outlet: DN250 Sludge: DN150 Vent: DN100 |
L/L1: 12.5/11.4 W/W1: 4.4/3.4 H/H1: 2.9/2.4 |
10000 | 130000 |
Dissolved air flotation process flow


The effectiveness of DAF units lies in their ability to handle a variety of wastewater streams, making them indispensable across multiple industries. Whether in industrial settings dealing with complex contaminants or municipal systems facing large volumes of urban runoff, DAF units prove their versatility and efficiency. They are particularly renowned in industries such as food and beverage production, where they handle organic matter and fats with ease, and in the oil and gas sector, where the separation of hydrocarbons is critical. Furthermore, the technology is adaptable, with configurations allowing for the introduction of various chemicals to optimize performance based on specific treatment needs.

The environmental impact of DAF systems is generally positive, particularly in minimizing water pollution. By enabling the removal of over 90% of harmful components from industrial effluents, DAF systems contribute to cleaner water bodies and reduced environmental pollution. Moreover, reduced chemical usage and advancements in energy-efficient designs further enhance the sustainability of DAF technology.
Dissolved air flotation application
Dissolved-air flotation processes have diverse applications across multiple industrial settings. Common industries benefiting from DAF technology include:
Food and Beverage: The food processing industry utilizes DAF systems to treat wastewater containing high concentrations of fats, oils, and food particles.
Pulp and Paper: DAF is employed to handle process water and to remove suspended solids, enhancing the quality of effluents.
Petroleum and Petrochemical: In these sectors, DAF systems act to remove oils and greases from produced water, significantly reducing environmental impact.
Wastewater Treatment Plants: Municipal treatment facilities use DAF to optimize sludge management and enhance overall treatment efficiency.

Contact Us for a Consultation

Name: Ashely Li
Mobile:+8613961861780
Tel:+8613961861780
Whatsapp:8613961861780
Email:info@dagyee.com
Add:Room 302, Building 11-4, Hongyi Road, Xinan Town, Xinwu District, jiangsu Province, China